Market Model
All trading executed on OMIP, as well as the clearing process on OMIClear, are anonymous. This means that the market participants do not have any information about the buyers or sellers identities. In the same way, during the clearing process, the agents never know who hold the positions, or what those positions are in disaggregated terms.
This concept is widened to include the registration of OTC transactions, where only the parties involved know each other, or if they use an intermediary, may maintain total anonymity.
This model is extremely useful, as it allows, each participant, to formulate expectations relative to price variation based on strategies and positions which titularity is not identified by the other participants.
All the buy and sell offers are public to participants. Consequently, they may exploit eventual disparities resulting from the gap between the supply and demand of each product. Besides this, it is possible to carry out leverage between different contracts without discriminating between agents, creating excellent conditions for determining fair prices.
As managing entity, OMIP tries to create the best conditions to promote high levels of liquidity, namely by promoting Market Makers intervention that assures the existence of buy and sell offers during most part of the trading session.
Through novation, all operations carried out on OMIP and registered at OMIClear, are guaranteed by this entity as Clearing House of the market. Thus, OMIClear ensures the multilateral clearing of positions, significantly reducing the various risks that affect the operations, such as credit, settlement, systemic and operational risk. This model fulfils a structural role, as it allows the coexistence of market agents of different sizes, risk exposure, trading areas without discriminating geographically.
OMIP is a Regulated Market operator that provides a trading platform for energy derivatives products, namely Futures, Forwards, Swaps, Options and FTR, the underlying asset of which is electricity and natural gas. In electricity, currently OMIP offers:
- Spanish Power: Futures, Swaps, Forwards and Options.
- Portuguese Power: Futures, Swaps
- German Power: Futures
- French Power: Futures
In natural gas OMIP lists futures contracts with reception or delivery at the Spanish virtual trading point PVB-ES, which are available for registration and clearing of bilateral transactions.
OMIClear - The Iberian Energy Clearing House - takes on the role of Clearing House and Central Counterparty in all the operations executed on the market managed by OMIP, being able to also clear trades on the OTC market or even other markets that have, as underlying assets, energy based products, or such like.
OMIP and OMIE hold a 50% stake each in OMIClear.
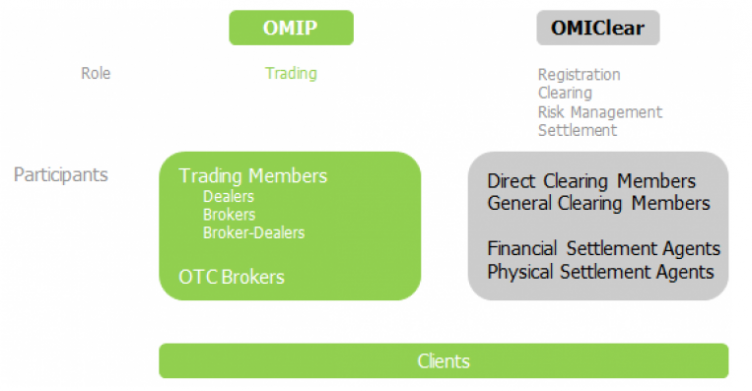
There is only one type of member on OMIP - Trading Member - with the exclusive role of creating orders and trading. However it is able to take on different statuses. OMIP also recognises OTC Brokers, although not being market members, provides OTC transaction intermediary services. For more details, please see Member Types section.
On the OMIP Trading Platform, futures contracts are traded. All the elements of these contracts are standardised (e.g. volume, underlying, minimum price variation). Therefore, when a participant opens a position, it needs only to choose the contract it will trade, the respective quantity and the price (except if it is a "market offer"). A key characteristic of these contracts is based on the fact that they have daily mark-to-market.
The operations carried out on OMIP are registered in trading accounts and simultaneously registered in clearing accounts, through which the financial settlement of the contracts is assured.
After opening a position on a Future, a participant has a number of alternatives to close that position:
- Carry out an opposite operation (if initially it bought, then it needs to sell, if it initially sold, it needs to buy) on the same Futures contract;
- Leave the position open until the contract’s maturity:
- If the positions are registered in the physical trading account, the information on the respective net position will be sent to OMEL to be integrated in the Day-Ahead Market at instrumental price.
- If not, there will be a purely financial settlement based on the difference between the spot reference price and the trading settlement price on the last trading day.
During the trading period, it is also possible to carry out operations on Futures contract from different series, allowing the management of market risk, cancelling or minimising portfolio risk. The same applies to a position on a contract that is in its delivery period.
The trading session is made up of 3 consecutive phases:
- Opening: beginning period of the Trading Day activity, during which the trading members can interact on the trading platform only to eliminate offers included in the central order book and create, modify or eliminate orders from the local order book, but they cannot execute operations.
- Trading: active period of the session, during which operations are allowed to be executed, by continuous or by fixing, and where the trading members are able to access the consultation, introduction, modification and cancelling of offers.
- Closing: final period of trading day activity, where the trading members are able to do the same as during the Opening Phase.
All the orders introduced onto the OMIP Trading Platform are valid if within the pre-established price limits. If a Trading Member inputs an offer with a higher (lower) price than the maximum (minimum) price limit defined for the contract in question, the Trading platform considers the order invalid by rejecting it.
The market participants can and should set up filters to control the volume of orders (maximum and minimum) and the respective price (maximum variation compared with the market price).
There are various types of accounts, namely, trading, clearing, financial settlement and physical settlement accounts. This account structure is extremely flexible, able to satisfy the most demanding market needs and configurations.
